We’ve all come home from the supermarket and cut into an onion, only to find that it has a mushy brown ring on the inside. And then there are the times when you pull an onion from the pantry and notice signs of mold on the skin. What do you do in those cases? Can you simply remove the blighted layers, or do you need to discard the whole bulb? And is there a way to tell if an onion is bad before you buy it or try to cook with it?
Sign up for the Cook’s Insider newsletter
The latest recipes, tips, and tricks, plus behind-the-scenes stories from the Cooks Illustrated team.Email addressAmericas Test Kitchen will not sell, rent, or disclose your email address to third parties unless otherwise notified. Your email address is required to identify you for free access to content on the site. You will also receive free newsletters and notification of Americas Test Kitchen specials.
To answer these questions and more, I contacted two experts: Dr. Bhabesh Dutta, associate professor and extension vegetable disease specialist at the University of Georgia, and Nick Frillman, local food systems & small farms educator—Livingston, McLean and Woodford Counties—University of Illinois Extension.
Is It Safe to Eat Moldy Onions?
Molds proliferate in moist environments and tend to rot the bulb from the outside in. There are many types and colors of mold that can develop on onions—mostly on the outer scales or just beneath the papery layer—said Dutta, and black and gray molds are quite common.
Per the USDA, it’s OK to use onions that have a little black mold (Aspergillus niger) on the outside after rinsing them under cool running water or cutting off the moldy area to remove as many spores as possible.
Onions that are heavily molded or that contain other colors of mold (including gray, white, or blue) should be discarded as they are likely contaminated below the surface.
Steak Baked inside of an Onion (NSE Too)
FAQ
What is inside an onion?
What is the middle of the onion called?
Can I eat the middle of onion?
What is the brown stuff inside my onion?
What is an onion made of?
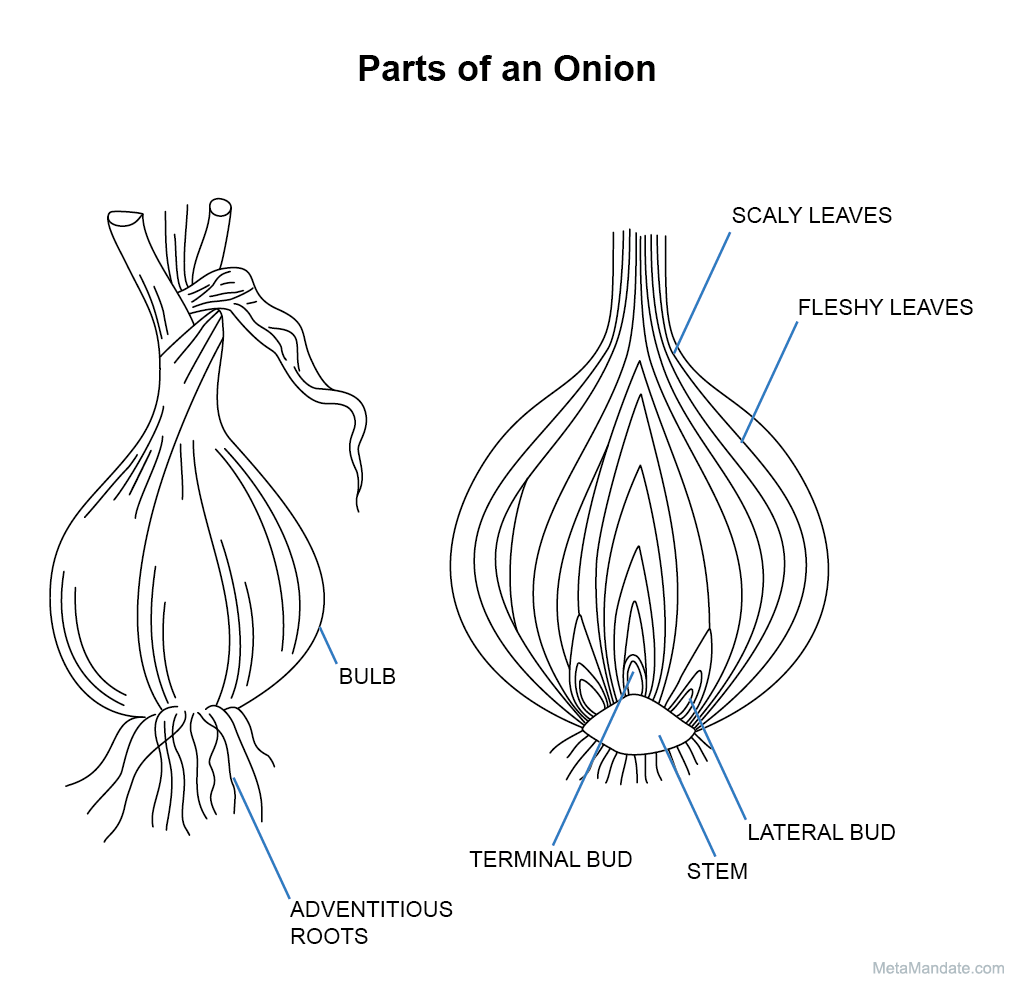
An onion is composed of several layers of thin, papery skin that surround the fleshy, edible bulb. The bulb is made up of concentric layers that are separated by a thin membrane. Each layer of the bulb is composed of tightly packed, fleshy leaves that are rich in nutrients and flavor.
What is the protein content in onions?
Onions do not contain a particularly high amount of protein, about 2 grams in 200 grams. However, onions contain high levels of vitamin B6, which helps protein absorption.
What are the outer layers of an onion?
The outer layers protect the inner layers and provide a barrier against external pathogens and environmental stressors. The inner layers, also known as scales, are responsible for storing nutrients and water. They are fleshy and contain a higher concentration of sugars, giving the onion its characteristic taste.
What are the different parts of an onion plant?
Discover the different parts of an onion plant, including its roots, bulb, foliage, and flowering stalk. Explore the functions of each plant part and understand the layers that make up an onion bulb. The anatomy of an onion plant consists of various parts that work together to support its growth and survival.
