Chloroxylenol is used in consumer products, increasingly since the ban of triclosan, triclocarban, and other harmful antimicrobials in hand soaps by the FDA in 2017 and 2018. However, don’t get too excited opting for products with this ingredient. The safety of chloroxylenol remains uncertain, and there is evidence to suggest it is a potential endocrine disruptor, deeming chloroxylenol a not-so-great replacement after all.
Chloroxylenol was first introduced as a fungicide in the U.S. in 1959 [10] and has long been used in household disinfectants and topical over-the-counter medicines.[7]
Following the FDA ban of triclosan, triclocarban, and other antimicrobial ingredients in soaps in 2017 and 2018, chloroxylenol was one of many compounds used to replace these active ingredients. The three most commonly used replacements for triclosan and triclocarban include chloroxylenol, benzalkonium chloride, and benzethonium chloride. [7] The FDAs rulemaking on chloroxylenol was deferred to allow more time for research into its safety and efficacy. In the meantime, it is still used in consumer products, regardless of the uncertainty surrounding its safety.
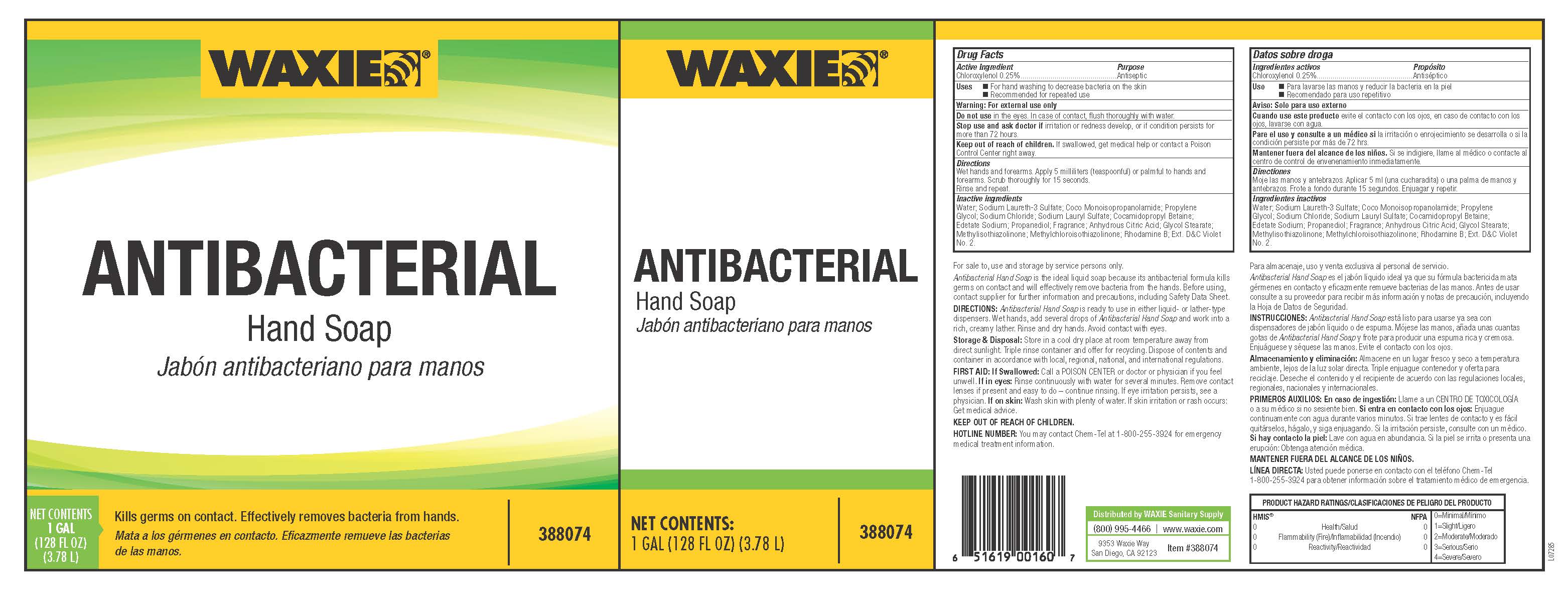
Chloroxylenol is an antibacterial chemical mostly found in hand soap and hand sanitizer, but has also long been used in household disinfectants and topical over-the-counter medicines.
The European Union classifies chloroxylenol as a skin and eye irritant, and skin sensitizer. [4] It is also toxic to aquatic life. Although research into its ecotoxicity is limited, chloroxylenol has been chronically linked to DNA damage, reproductive toxicity, and neurotoxicity in aquatic species. [1] [7] [8] The enhanced prevalence of chloroxylenol in consumer products has raised environmental concern, considering increased environmental occurrence is expected as a result of its wider expansion to everyday consumer products following the ban of triclosan and triclocarban. [2]
In 2011, it was placed on the TEDX List of Potential Endocrine Disruptors for its connection to other phenolic additives that were already established endocrine disruptors. [9] Since then, research on chloroxylenol has linked the substance to hormone disruption and testicular toxicity. [3] Some research suggests chloroxylenol may also play a role in antibiotic resistance, although findings on this topic are limited and inconsistent. [5] [6]
Humans are primarily exposed to chloroxylenol through dermal contact (e.g., using hand sanitizers), and chloroxylenol has been detected in urine samples. [8] Its widespread occurrence in aquatic environments around the world is indicative of prevalent human exposure. [8]
The available research on chloroxylenol is conflicting, and more studies are necessary to better understand the impacts of its widespread use on human health, which is largely unknown. Its increased use in recent years and evidence of toxic effects on the environment are enough to warrant caution and avoidance of this substance in consumer products. Because of chloroxylenol’s potential endocrine active capabilities, [3] [9] MADE SAFE exercises the precautionary principle and does not permit the ingredient in certified products.
A quantitative human risk assessment of chloroxylenol was conducted for liquid hand and dishwashing soap products used by consumers and health-care workers. The toxicological data for chloroxylenol indicate lack of genotoxicity, no evidence of carcinogenicity, and minimal systemic toxicity.
Item added to your cart
Chloroxylenol is used in consumer products, increasingly since the ban of triclosan, triclocarban, and other harmful antimicrobials in hand soaps by the FDA in 2017 and 2018. However, don’t get too excited opting for products with this ingredient. The safety of chloroxylenol remains uncertain, and there is evidence to suggest it is a potential endocrine disruptor, deeming chloroxylenol a not-so-great replacement after all.
Chloroxylenol was first introduced as a fungicide in the U.S. in 1959 [10] and has long been used in household disinfectants and topical over-the-counter medicines.[7]
Following the FDA ban of triclosan, triclocarban, and other antimicrobial ingredients in soaps in 2017 and 2018, chloroxylenol was one of many compounds used to replace these active ingredients. The three most commonly used replacements for triclosan and triclocarban include chloroxylenol, benzalkonium chloride, and benzethonium chloride. [7] The FDAs rulemaking on chloroxylenol was deferred to allow more time for research into its safety and efficacy. In the meantime, it is still used in consumer products, regardless of the uncertainty surrounding its safety.
Chloroxylenol is an antibacterial chemical mostly found in hand soap and hand sanitizer, but has also long been used in household disinfectants and topical over-the-counter medicines.
The European Union classifies chloroxylenol as a skin and eye irritant, and skin sensitizer. [4] It is also toxic to aquatic life. Although research into its ecotoxicity is limited, chloroxylenol has been chronically linked to DNA damage, reproductive toxicity, and neurotoxicity in aquatic species. [1] [7] [8] The enhanced prevalence of chloroxylenol in consumer products has raised environmental concern, considering increased environmental occurrence is expected as a result of its wider expansion to everyday consumer products following the ban of triclosan and triclocarban. [2]
In 2011, it was placed on the TEDX List of Potential Endocrine Disruptors for its connection to other phenolic additives that were already established endocrine disruptors. [9] Since then, research on chloroxylenol has linked the substance to hormone disruption and testicular toxicity. [3] Some research suggests chloroxylenol may also play a role in antibiotic resistance, although findings on this topic are limited and inconsistent. [5] [6]
Humans are primarily exposed to chloroxylenol through dermal contact (e.g., using hand sanitizers), and chloroxylenol has been detected in urine samples. [8] Its widespread occurrence in aquatic environments around the world is indicative of prevalent human exposure. [8]
The available research on chloroxylenol is conflicting, and more studies are necessary to better understand the impacts of its widespread use on human health, which is largely unknown. Its increased use in recent years and evidence of toxic effects on the environment are enough to warrant caution and avoidance of this substance in consumer products. Because of chloroxylenol’s potential endocrine active capabilities, [3] [9] MADE SAFE exercises the precautionary principle and does not permit the ingredient in certified products.
Hand Sanitizers and Soaps Put to the Test
FAQ
Is chloroxylenol safe in soap?
What is the risk of chloroxylenol?
Is chloroxylenol safe for humans?
What is the healthiest hand soap to use?
Is chloroxylenol safe in rinse-off liquid antimicrobial hand soap?
A human health risk assessment was conducted to evaluate the safety of chloroxylenol used as an active ingredient in rinse-off liquid antimicrobial hand soaps and dish soaps by consumer (adults and children) and in rinsed off antimicrobial liquid hand soaps by health-care workers.
Is chloroxylenol in liquid soap safe?
The finding that all MOEs were greater than 100 despite the use of many health-protective assumptions indicates low potential for harm related to consumer or health-care worker exposure to chloroxylenol in liquid soaps. The relatively high MOEs identified here also provide some reassurance related to limitations in the underlying database.
Is chloroxylenol safe?
In the meantime, it is still used in consumer products, regardless of the uncertainty surrounding its safety. Chloroxylenol is an antibacterial chemical mostly found in hand soap and hand sanitizer, but has also long been used in household disinfectants and topical over-the-counter medicines.
Is chloroxylenol a toxicity hazard?
The existing toxicity data for chloroxylenol have limitations, but taken together the data are adequate for evaluation of the risks associated with consumer and health-care exposure to chloroxylenol in hand soap or dish soap.
