Apple cider vinegar has known health benefits, but you can have too much of a good thing. Watch your intake, and be aware of apple cider vinegar side effects, such as delayed stomach emptying, nausea, or erosion of tooth enamel.
Apple cider vinegar is a natural tonic. It has several health benefits that scientific studies in humans support.
Learn more about apple cider vinegar’s potential side effects and how to consume apple cider vinegar safely.
Hey there, folks! If you’ve been sippin’ on apple cider vinegar (ACV) thinkin’ it’s gonna jack up your potassium levels, I’ve got some news for ya. Spoiler alert: it ain’t the potassium powerhouse you mighta heard about. At our lil’ corner of health chatter, we’re all about keepin’ it real, so let’s dive into this question—does apple cider vinegar increase potassium?—and unpack the facts with no fluff. Stick with me, and I’ll break it down simple, with some handy tips and truths to keep your diet game strong.
What’s the Big Deal with Potassium Anyway?
Before we get into the ACV hype let’s chat about why potassium even matters. This mineral is like the unsung hero of your body. It’s keepin’ things runnin’ smooth in a buncha ways
- Muscle Power: Helps your muscles contract, includin’ your heart. No potassium, no pumpin’ right.
- Nerve Signals: Keeps your nerves talkin’ to each other so you can move and think quick.
- Blood Pressure Balance: Works to keep that pressure in check, fightin’ off the risks of goin’ too high.
- Fluid Control: Makes sure your body ain’t holdin’ too much water or gettin’ dehydrated.
Your body needs a good chunk of it daily—around 4700 mg for most adults. If you’re runnin’ low, you might feel weak tired, or even get weird heart rhythms. That’s why peeps are always huntin’ for ways to get more. But is ACV the answer? Let’s see.
Apple Cider Vinegar: What’s in This Magic Juice?
I’ve seen folks swear by ACV like it’s some kinda miracle in a bottle. Made from fermented apples, it’s got this tangy kick thanks to acetic acid, which is the star player behind a lotta its supposed perks. People chug it for weight loss, better digestion, clearer skin—you name it. But when it comes to potassium, does it deliver?
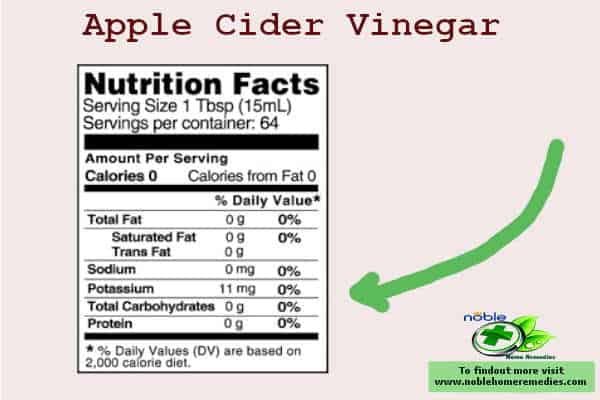
Here’s the straight-up truth: ACV has potassium, but it’s a tiny, almost laughable amount. We’re talkin’ about 11 mg per tablespoon. Compare that to your daily goal of 4,700 mg, and it’s like bringin’ a toothpick to a sword fight. You’d have to down buckets of the stuff to even make a dent, and trust me, that ain’t a good idea (more on that later).
Busting the Myth: Does It Increase Potassium?
So, to answer the big question right off the bat—no, apple cider vinegar doesn’t significantly increase your potassium levels. If you’re relyin’ on it to hit your daily needs, you’re barkin’ up the wrong tree. That trace amount ain’t gonna move the needle, and honestly, there are way better ways to get this mineral into your system.
In fact, goin’ overboard with ACV might even mess with your potassium in the wrong direction Some folks, especially those with kidney troubles, could see levels drop ‘cause of its acidity and mild diuretic effect—meanin’ it makes ya pee more, potentially flushin’ out electrolytes. Ain’t that a kicker? Instead of boostin’, you might be losin’ what you’ve got.
How Does ACV Stack Up Against Real Potassium Champs?
Let’s put this into perspective with a lil’ comparison. I’ve thrown together a quick table to show ya how ACV measures up against some legit potassium-heavy hitters. Check this out:
| Food Source | Potassium Content (mg per serving) |
|---|---|
| Banana (1 medium) | 422 mg |
| Baked Potato (with skin) | 926 mg |
| Spinach (cooked, 1 cup) | 839 mg |
| Avocado (1 medium) | 708 mg |
| Apple Cider Vinegar (1 tbsp) | 11 mg |
See what I mean? One banana blows ACV outta the water. You’d need to chug like 40 tablespoons of vinegar to match that, and who’s got the stomach for that? Not me, that’s for sure. If you’re lookin’ to up your potassium, skip the vinegar aisle and head straight for the produce section.
Why Do People Think ACV Helps with Potassium?
I get why there’s confusion. ACV’s got this health halo ‘round it, and peeps love a quick fix. Some think since it’s made from apples, it’s gotta be packed with nutrients like potassium. Others reckon the acetic acid might help your body soak up potassium from other foods. But here’s the deal—there ain’t much science backin’ that up. It’s mostly just wishful thinkin’ and internet whispers.
At our blog, we’ve seen all kinda myths floatin’ around, and this is one of ‘em. The reality? ACV’s potassium content is too dang low to matter, and any absorption boost is still unproven. Don’t fall for the hype—stick to what works.
Could ACV Actually Lower Potassium?
Now, here’s where it gets a bit dicey. While ACV won’t boost your potassium, overdoin’ it might do the opposite. That acetic acid can mess with your body’s balance if you’re guzzlin’ it like water. Here’s a few ways it could happen:
- Acidity Impact: Too much acid might tweak how your body handles minerals, maybe even pushin’ out more potassium through pee.
- Diuretic Vibes: Some say it acts a bit like a diuretic, makin’ you lose fluids and electrolytes faster than normal.
- Kidney Strain: If your kidneys ain’t in top shape, they struggle to manage potassium anyway, and ACV could add to the trouble.
I ain’t sayin’ a splash in your salad dressin’ gonna wreck ya, but chuggin’ it straight or takin’ huge doses daily? That’s askin’ for issues. I’ve heard of folks gettin’ throat burns or messed-up teeth from overusin’ it, so let’s not even go there.
Who Needs to Watch Out?
Not everyone’s gotta worry, but some of y’all should keep an eye out. If you’re in one of these groups, ACV might not be your best buddy:
- Kidney Issues: If your kidneys are strugglin’, they can’t filter stuff like potassium right. Addin’ ACV could make things worse.
- On Certain Meds: Some pills, like diuretics for blood pressure, already mess with potassium. Mixin’ in ACV might tip the scales.
- Sensitive Stomachs: Got acid reflux or tummy troubles? That vinegar burn ain’t gonna help.
- Pregnant or Nursin’: It’s usually fine in small bits, but check with your doc before makin’ it a habit.
I always say, when in doubt, chat with your healthcare peeps. They’ll steer ya right based on your own health story.
So, What’s ACV Good For Then?
Alright, if it ain’t a potassium booster, why even bother with apple cider vinegar? Fair question! I’ve tinkered with it myself in the kitchen and for health kicks, and there’s some cool stuff it might do. Keep in mind, not all of this is set in stone—science is still catchin’ up—but here’s the buzz:
- Blood Sugar Help: Some small studies hint that takin’ ACV with meals could lower blood sugar spikes, especially for folks with diabetes. It might help insulin work better.
- Feelin’ Full: It could slow down how fast your stomach empties, makin’ ya feel satisfied longer. Handy if you’re watchin’ calories.
- Weight Loss Aid: There’s a tiny bit of evidence that pairin’ it with a good diet and exercise might nudge the scale down a tad more than just diet alone.
- Heart Health Perks: A few peeps found it might lower bad fats in your blood and bump up the good kind, though we need more proof.
- Germ Fighter: That acetic acid’s got a knack for killin’ off some nasty bacteria, which is why it’s been used as a cleaner or preservative way back when.
I’ve mixed a spoonful in water before a big meal, and it does seem to keep me from overeatin’ sometimes. But it ain’t magic—ya still gotta eat right and move your butt.
How to Use ACV Without Messin’ Up
If you’re still keen on ACV for its other perks, let’s make sure you’re doin’ it safe. I’ve made the mistake of sippin’ it straight once, and lemme tell ya, my throat wasn’t happy. Here’s how to roll with it:
- Dilute It, Man: Mix 1-2 tablespoons in a big glass of water. Cuts the burn and saves your teeth from that acid.
- Dress It Up: Use it as a salad dressin’ with some olive oil. Tastes great and keeps portions in check.
- Don’t Overdo: Stick to a couple spoonfuls a day max. More ain’t better—it’s just trouble.
- Listen to Your Body: If ya feel weird—stomach aches, weird tiredness—ease off and check in with a doc.
We wanna keep things fun and healthy, not turn your gut into a war zone. So, play it smart with this stuff.
Where to Get Your Potassium Fix Instead
Since ACV ain’t the potassium hero we hoped, let’s talk real food that’ll get ya there. I’ve got a soft spot for some of these, and they’re easy to toss into your meals. Here’s your go-to list:
- Bananas: Grab one for a snack—over 400 mg in a single fruit. I throw ‘em in smoothies all the time.
- Sweet Potatoes: Roast ‘em up with a lil’ salt. You’re lookin’ at near 700 mg per spud.
- Spinach: Saute or toss in a salad. A cup of cooked greens nets ya over 800 mg.
- Avocados: Smash on toast or slice into a sandwich. One’s got over 700 mg, plus good fats.
- Beans and Lentils: Kidney beans, black beans—whatever ya fancy. A cup can hit 600-800 mg easy.
I’ve been known to whip up a mean bean chili that’s loaded with potassium, and it’s a crowd-pleaser. Stock your kitchen with these, and you won’t even think twice about ACV for this nutrient.
Wrappin’ It Up: The Real Deal on ACV and Potassium
So, let’s circle back to where we started. Does apple cider vinegar increase potassium? Nah, not in any way that counts. It’s got a measly bit of the stuff, nowhere near what you need, and if you overdo it, you might even lose more than ya gain. I’ve seen too many folks get caught up in the hype, thinkin’ a shot of vinegar’s gonna solve all their health woes. It just ain’t so.
Instead, we’re rootin’ for ya to focus on the good stuff—real foods like bananas, potatoes, and greens that pack a potassium punch. ACV’s got its place, maybe for a blood sugar tweak or a salad zing, but don’t make it your go-to for minerals. Keep it moderate, keep it safe, and always double-check with your health crew if somethin’ feels off.
Got thoughts or tricks with ACV you wanna share? Drop ‘em below—I’m all ears! And hey, if you’re diggin’ this kinda no-nonsense health talk, stick around. We’ve got plenty more where this came from. Let’s keep eatin’ smart and livin’ well together!
What are the negative effects of apple cider vinegar?
Apple cider vinegar has been reported to cause some side effects. This is particularly true when it’s consumed in large doses.
Although small amounts are generally fine and healthy, consuming too much can be harmful and even dangerous.
What is apple cider vinegar?
Apple cider vinegar is made by combining apples with yeast.
The yeast converts the sugar in the apples into alcohol. Bacteria are then added to the mixture and ferment the alcohol into acetic acid (1).
Acetic acid makes up 5–6% of apple cider vinegar. It’s classified as a “weak acid” but still has fairly strong acidic properties when it’s concentrated.
In addition to acetic acid, vinegar contains water and trace amounts of other acids, vitamins, and minerals (1).
Several studies in animals and humans have found that acetic acid and apple cider vinegar may promote fat-burning and weight loss, decrease blood sugar levels, increase insulin sensitivity, and improve cholesterol levels (2, 3, 4, 5).
Unfortunately, human studies supporting the daily use of apple cider vinegar are lacking, and more research is needed (6).
Apple Cider Vinegar and Mineral Absorption
FAQ
Is apple cider vinegar high in potassium?
What is the downside of apple cider vinegar?
What happens if you drink apple cider vinegar every morning?
Takeaway. Drinking apple cider vinegar in small amounts can be harmless and may be beneficial to health based on limited research. That said, there’s no evidence that drinking in the morning is better than consuming it at any other time.
Can apple cider cause low potassium?
Does apple cider vinegar lower potassium levels?
1. Lower Potassium Levels When used in large quantities over a long period of time, apple cider vinegar can decrease your potassium levels. 1 Low potassium levels (hypokalemia) pose a risk to the heart’s and nervous system’s electrical systems, causing signaling issues.
Can licorice and apple cider vinegar cause hypokalemia?
Taking licorice and apple cider vinegar together may increase your risk for hypokalemia. Talk with your healthcare provider before taking apple cider vinegar and licorice. They will likely monitor your potassium levels or recommend a different treatment option.
Can you take apple cider vinegar with a diuretic?
Some diuretics also lower potassium levels. If you take apple cider vinegar with a diuretic that lowers potassium, you are at a higher risk of experiencing hypokalemia. Hypokalemia occurs once your potassium level is below about 3.5 millimoles per liter (mmol/L) of blood.
Can you eat too much apple cider vinegar?
Since apple cider vinegar is not a concentrated source of potassium, the risk of consuming excessive potassium from it is low. However, excessive consumption of any product may have adverse effects, and moderation is always key. 10.
Can apple cider vinegar cause osteoporosis?
A paper was published detailing health issues found in a patient who had consumed 8 ounces of apple cider vinegar diluted with water every day over the span of six years. She was found to have low potassium levels and was diagnosed with osteoporosis, a rareity in someone as young as the 28-year-old. 2
Does apple cider vinegar have acetic acid?
Apart from acetic acid, apple cider vinegar also contains trace amounts of potassium, as well as other beneficial compounds like antioxidants and amino acids. Do you like this article? Potassium is an essential nutrient that the body requires for proper functioning.
